Immune boosting explains regime-shifts in prevaccine-era pertussis dynamics
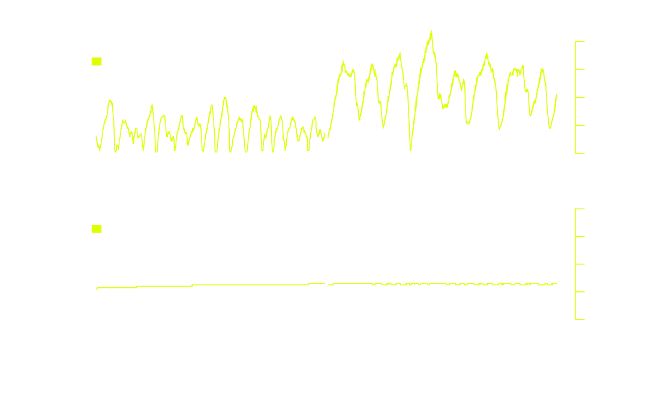
Understanding the biological mechanisms underlying episodic outbreaks of infectious diseases is one of mathematical epidemiology’s major goals. Historic records are an invaluable source of information in this enterprise. Pertussis (whooping cough) is a re-emerging infection whose intermittent bouts of large multiannual epidemics interspersed between periods of smaller-amplitude cycles remain an enigma. It has been suggested that recent increases in pertussis incidence and shifts in the age-distribution of cases may be due to diminished natural immune boosting. Here we show that a model that incorporates this mechanism can account for a unique set of pre-vaccine-era data from Copenhagen. Under this model, immune boosting induces transient bursts of large amplitude outbreaks. In the face of mass vaccination, the boosting model predicts larger and more frequent outbreaks than do models with permanent or passively-waning immunity. Our results emphasize the importance of understanding the mechanisms responsible for maintaining immune memory for pertussis epidemiology.
